Comparing the Environmental Impacts of Single-Use Bioreactors vs. Stainless Steel

In this article, we look at environmental impacts of single use bioreactors vs. their stainless steel counterparts:
- Review literature on the environmental impacts of bioprocessing.
- Examine wastewater streams as an example of the environmental impact of clean‑in‑place/steam‑in‑place (CIP/SIP).
- Discuss process intensification as a means of reducing the overall environmental impact of bioprocessing.
Studies on environmental impacts of bioprocessing
- CIP/SIP between each batch requires a standard amount of energy and supporting equipment
- Single‑use plastics are being compared to multiuse stainless steel
- Single‑use components arrive at the pharmaceutical manufacturing site pre‑sterilized by irradiation
- Single‑use components are disposed of via hazardous waste incineration (some studies assume heat recovery; it is not shown to have a significant impact on the overall energy costs)
Study 1: Stainless steel bioreactors are more harmful to humans and ecosystems
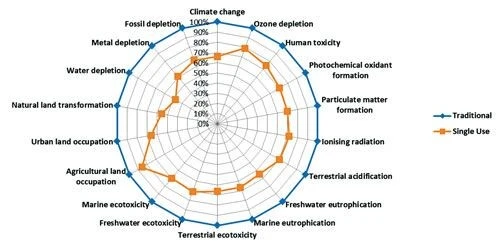
Results & analysis: The authors evaluated the full process trains at 100 L, 500 L, and 2,000 L scales for a 10‑batch campaign. They used 18 categories to assess environmental impact, including human toxicity as well as depletion of water, metal, ozone, and fossil. For 2,000 L volumes, the single‑use bioreactors proved to be advantageous over multiuse bioreactors in each of the 18 categories, as shown in Figure 1.
Study 2: CIP/SIP accounts for over half of the total energy consumption of stainless steel skids
- Single‑use plastics are assumed to be made entirely of polypropylene
- Stainless steel bioreactors have a lifetime of 600 production batches, but the required liquid and air filters must be regularly replaced.
- Single‑use biocontainers are housed in stainless steel totes without vent filters.
- Single‑use capsule filters inside stainless steel housings are used instead of standard liquid and exhaust gas filters.
- Single‑use membrane absorber capsules are used instead of standard chromatography columns and resins.
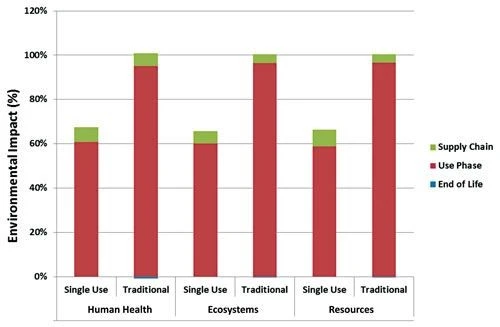
Results & analysis: Table 1 shows a summary of the energy calculations for single‑use plastic systems compared to multiuse stainless steel. Materials production refers to the energy cost of manufacturing the components for the two solutions; sterilization refers to SIP between batches for stainless steel systems or pre-sterilizing components by irradiation for single‑use systems; and cleaning refers to CIP for reusable skids, most often using a combination of pyrogen‑free distilled water, sodium hydroxide, and phosphoric acid in standard, pre‑determined quantities.
SIP calculations assumed a steam generator output of 500 kW/h, and 100 L of water necessary to provide 30 minutes of steam at 130oC, with SIP between each batch. In contrast, single‑use components are irradiated by the manufacturer and then disposed of after use. This study found that sterilizing multiuse skids between batches is over 6x more energy intensive than sterilizing single‑use components before use.
The largest energy expenditure in traditional bioreactor systems is in producing the pyrogen‑free distilled water necessary for cleaning. The 4,900 MJ which this study determined to be necessary for cleaning multiuse systems lies in sharp contrast to 0 MJ required for single‑use components, which do not need to be cleaned.
Key findings: Over a lifetime of use, single‑use bioreactors are significantly less energy intensive than multiuse bioreactors. CIP/SIP accounts for the vast majority of the energy requirements for traditional bioreactor skids, meaning the elimination of inline cleaning and sterilization is the key environmental advantage of single‑use systems.
Example: waste streams resulting from CIP/SIP
Standard cleaning solutions for reusable stainless steel and plastic components include 1 M sodium hydroxide, 1 M phosphoric acid, pyrogen‑free distilled water, buffers, cleaning agents, and steam. Sanitation solutions are usually diluted bleach, and wipe‑down solutions are generally quaternary disinfectants. These solutions must then all be rinsed several times over — creating chemical runoffs which must be properly handled.
To address the issues associated with chemical waste streams, regulatory drivers have moved pharmaceutical facilities from chemical sanitation to steam sanitation. Steam sanitation creates less chemical runoff and less energy is required to treat the waste streams. However, the energy cost of steam generation can be great enough to offset these advantages.
Impact of CIP/SIP and the role of process intensification as a remedial solution
Despite their environmental advantages, single‑use skids are not always feasible, for reasons ranging from process scale to extreme operating conditions to fluid incompatibilities. Process intensification therefore provides a simple means by which to introduce significant energy savings into the plant.
Hybrid systems provide a practical, environmentally-conscious design
Hybrid systems, consisting of a combination of single‑use and multiuse skids, can offer a unique opportunity to reduce a plant’s environmental footprint without requiring a total overhaul of the manufacturing process. This allows system designers to take advantage of skids with appropriate single‑use solutions, while recognizing their limitations in other areas.
Skids designed for easy CIP/SIP lead to less water and steam, and fewer chemicals
Making more cleanable skids would result in CIP/SIP procedures that require less water and fewer chemicals — resulting in less wastewater treatment, less steam generation, and an all‑around lower energy cost of cleaning. Skids allowing for in‑line buffer dilution would allow for smaller buffer holding tanks, resulting in less equipment to clean and sterilize and time savings from not needing to move various pieces around the facility. This in turn can lead to smaller facility sizes, which have lower HVAC costs.
Operator training means producing only the wastes which are strictly necessary
Expanding training for operators is a simpler step for leaner processing and achieving process intensification. Overages are built into standard operating procedures, but extra‑cautious operators may want to add an extra rinse. Training operators closely on the SOPs and the reasoning behind each step can prevent unnecessary rinsewater or buffer production — and reduce inventory to only what is strictly necessary. This is particularly useful given that refrigerant gases have a large environmental footprint. Together, these factors indicate that single‑use bioreactors compared to stainless steel are not the only factors in the overall environmental impact of bioprocessing.